Whether you’re a landlord of a commercial property or a tenant leasing commercial space, it’s important to understand the different types of commercial leases you may encounter during lease negotiations. Net, gross, and modified gross leases are not one-size-fits-all, as they determine how key expenses like property taxes, utilities, and maintenance costs are split between the tenant and landlord.
In this blog, we’ll break down some common commercial lease types, explaining how each one works and what it means for you during the leasing process.
Net Lease
A net lease is a type of commercial real estate lease where the tenant pays the base rent, along with some or all of the additional expenses associated with the property, including property taxes, insurance, and/or maintenance costs. The landlord covers any remaining expenses.
In net leases, the tenant typically pays their actual, proportionate share of the operating expenses as they fluctuate, unlike a modified gross lease, where certain expenses might be capped, fixed, or limited to specific items depending on the lease terms.
With net leases, landlords benefit from predictable net income, and tenants typically benefit from a lower base rent compared to gross leases. However, tenants are responsible for any unexpected increases in operating expenses that may arise. In some cases, landlords provide annual operating expense estimates to help tenants budget for these variable costs.
There are multiple types of net leases:
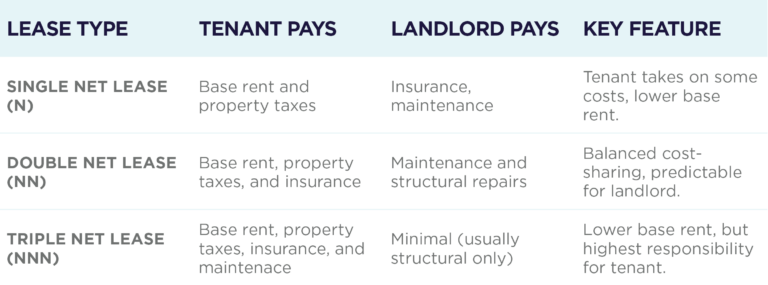
Single Net Lease
A lease where the tenant pays the base rent, plus the property taxes. The landlord covers the remaining expenses.
Net-Net Lease, Double Net Lease, or NN Lease
A lease where the tenant pays the base rent, plus property taxes and insurance. The landlord covers the remaining expenses.
Net-Net-Net Lease, Triple Net Lease, or NNN Lease
A lease where the tenant pays the base rent, plus property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs. The landlord’s expenses are limited. Triple net leases often result in less predictability for the tenant’s monthly payments.
Gross Lease (or Full-Service Lease)
A gross lease is a commercial lease agreement where the tenant pays one set amount to the landlord each month. The landlord covers most or all of the property-related expenses such as taxes, insurance, and maintenance.
Gross leases are common in offices. Since the tenant pays one fixed fee per month, it allows them to budget more accurately without planning for varying expenses month to month. It also makes it easier for the landlord to create a consistent environment across multiple tenants within the property for operations and maintenance.
While gross leases can simplify monthly rent for tenants and allow for easier maintenance for landlords, gross leases can also result in higher monthly rent for tenants to factor in the landlord’s operating costs.
Modified Gross Lease
A modified gross lease is a type of lease where the tenant pays the base rent along with a portion of the operating expenses, which is negotiated with the landlord. Unlike a net lease, the tenant’s share of operating expenses may be fixed, capped, or limited to specific items, depending on the terms of the lease. The landlord covers the remaining expenses.
Modified gross leases are often seen in multi-tenant office buildings, older properties, or small mixed-use spaces.
While a modified gross lease may bring more predictability than a net lease, it also isn’t as predictable as a full gross lease for budgeting, since certain expenses may vary greatly month-to-month.
Modified gross leases also allow for greater flexibility in negotiating which expenses are shared and how costs are allocated. However, the terms vary greatly from deal to deal, resulting in more complex negotiations.

At Cushman & Wakefield | Stevenson, our team of commercial real estate agents in Winnipeg has the market expertise to help both landlords and tenants determine the lease type that best meets their needs based on the property and asset class. Contact us today to connect with one of our agents.